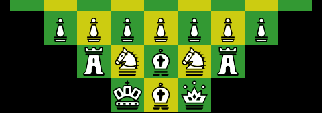
Modern Random Chess 64
The MRC64 variation is an 8x8 board adaptation of my 9x9 Modern Random Chess (MRC) game. Modern Random Chess 64 inherits from MRC the random setup, reverse symmetry, symmetric castling to either side, and the Bishop Adjustment Rule.Setup
 ....
....
 ....
....

All pieces are randomly placed in the player’s first rank, with the only restriction that the King must be between the two rooks. It is possible for both Bishops to be on the same color squares (dark or light squares). The opponents’ pieces are placed with reverse symmetry (White’s piece at a1 is equivalent to Black’s h8, White’s b1 to Black’s g8, White’s c1 to Black’s f8, White’s d1 to Black’s e8, and so on…)
There is a Bishop Adjustment rule that is in effect only in games when both Bishops start on the same color squares in the initial random setup. This rule allows players to move one of the Bishops to the opposite color, if they so desire.
There are 2,520 different legal starting positions in MRC64.
Reverse Symmetry
In a reverse symmetrical setup the piece at the square a1 for White, is the same as the piece at h8 for Black. The piece at b1 for White is the same as the one at g8 for Black, and so on. The Pawns are in the second row of each player’s side.
Let looks at another example, from both White and Black’s point of view:
 ....
....

In the MRC position on the left, from White’s point of view, the Queen is on the leftmost square next to a Rook, his 2nd Rook is on his rightmost square next to a Knight, the Bishops are on their traditional Orthodox Chess initial squares, the King has a Knight to his right, and so on. Also, from White’s point of view, his opponent’s opponents King is across the board from the Knight to his right, the Bishops are across the board to each other, the Queen is on the other corner of the same long diagonal as his own Queen, and you could continue to describe the position of the opponent’s pieces in relation of White’s own.
Now look at the same MRC position in the diagram on the right, but from Black’s point of view. Every single observation made from White’s point of view above, applies as well to the point of view from Black. That's reverse symmetry!
Pieces
Orthodox Chess pieces are exclusively used.Rules
Orthodox Chess rules apply when applicable. Modified Castling rules are below, as well as the new Bishop Adjustment Rule.Castling
Modern Random Chess allows each player to castle once per game, a move by potentially both the king and rook in a single move. The MRC castling
rules are based in the Fischer Random Chess rules.
In Modern Random Chess, depending on the pre-castling position on the castling King and Rook, the castling manoeuvre is performed by one of these four methods:
- Double-move castling: By on one turn making a move with the king and a move with the rook.
- Transposition castling: By transposing the position of the king and the rook.
- King-move-only castling: By making only a move with the king.
- Rook-move-only castling: By making only a move with the rook.
After castling, the rook and king's final positions are exactly the same positions as they would be in Maura’s Modern Chess. Thus, after c-castling (notated as O-Ob), the King is on the b-square (b1 for White and c8 for Black) and the Rook is on the c-square (c1 for White and c8 for Black). After g-castling (notated as O-Og), the King is on the g-square (g1 for White and g8 for Black) and the Rook is on the f-square (f1 for White and g8 for Black).
This table shows where the King and Rook end up and the notation for each type of castling.
| White castles a-side | b-castling | O-Ob | Kb1, Rc1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| White castles h-side | g-castling | O-Og | Kg1, Rf1 |
| Black castles a-side | b-castling | O-Ob | Kb8, Rc8 |
| Black castles h-side | g-castling | O-Og | Kg8, Rf8 |
However, castling may only occur under the following conditions, which are extensions of the standard rules for castling:
- Unmoved: The King and the castling Rook must not have moved before in the game, including a previous castling or a Bishop Adjustment.
- Un-attacked: All of the squares between the king's initial and final squares (including the initial and final squares) must not be under attack by any opposing piece.
- Vacant: All the squares between the king's initial and final squares (including the final square), and all of the squares between the rook's initial and final squares (including the final square), must be vacant except for the king and castling rook.
- Castling cannot capture any pieces.
- The king and castling rook cannot "jump" over any pieces other than each other.
- A player may castle at most once in a game.
- If a player moves his king or both of his initial rooks without castling, he may not castle during the rest of the game.
- In some starting positions, some squares can stay filled during castling that would have to be vacant in Modern Chess. For example, after c-castling (O-Oc), it's possible for to have a, b, and/or e still filled, and after g-castling (O-Og), it's possible to have e, h and/or i filled.
- In some starting positions, the king or rook (but not both) do not move during castling.
- In some starting positions, castling can take place as early as the first move.
- The king may not be in check before or after castling.
- The king cannot move through check.
- The king cannot jump over his own rook if and when said rook stands on a “checked†square.
- A King that has swapped places with a Bishop according to the Bishop Adjustment rule can no longer do castling for the rest of the game.
- A Rook that has swapped places with a Bishop according to the Bishop Adjustment rule can no longer castle with the King.
- Castling in MRC64 is symmetric to either side of the board. MRC64 Castling is like the Orthodox short castling (O-O) but to either side.
The Bishop Adjustment Rule
In those positions where the Bishops start up in the same color squares (either both on dark or light squares), players on their turn, are allowed to convert one (and only one) of their Bishops to the opposite color square by swapping places with any piece adjacent to them. Neither the Bishop nor the piece to be adjusted with may have moved before the Bishop swap. The Bishop adjustment will count as a single turn, and a move for both the Bishop and the piece swapped with.The Bishop Adjustment Rule is optional, and a player is not forced to use it. A player may choose to play with his Bishops on the same color squares if he so desires, even if his opponent chooses to adjust one of his Bishops.
Note that the Bishop Adjustment rule has the following consequences in MRC64:
- A Bishop on a corner may only adjust with the one piece adjacent to it.
- The Bishop is allowed to swap places with a Knight, the Queen, a Rook, and also with the King!
- If the Bishop Adjusts with a Rook, that rook will be considered to have moved, and King Castling with that rook will no longer be possible. King Castling with the other Rook will still be possible provided neither the second Rook nor the King have moved.
- If the Bishop Adjusts with the King, the King will be considered to have moved, and King Castling will no longer be available for the rest of the game.
- When adjusting with the King, the Bishop Adjustment is considered to be a “Bishop†move, and not a King move that enables a player to move out of check. If the King is in check, it is not legal to move out of check with a Bishop Adjustment.
Notes
Modern Random Chess 64 (MRC64) was created by José Manuel Carrillo-Muñiz, from Puerto Rico in 2008.
Game Courier Logs
Game Courier Logs for Games of Modern Random Chess 64To see actual games that have been played on-line, follow the link above. This 'user submitted' page is a collaboration between the posting user and the Chess Variant Pages. Registered contributors to the Chess Variant Pages have the ability to post their own works, subject to review and editing by the Chess Variant Pages Editorial Staff.
This 'user submitted' page is a collaboration between the posting user and the Chess Variant Pages. Registered contributors to the Chess Variant Pages have the ability to post their own works, subject to review and editing by the Chess Variant Pages Editorial Staff.
By Jose Carrillo.
Web page created: 2008-05-11. Web page last updated: 2008-05-11